How to Recycle Your Old Car Battery

A typical car battery has a life expectancy of less than five years. There are batteries that end up lasting much longer than that, but they might not work as efficiently after that point. Following replacement, a dead car battery must be disposed of properly to reduce the risks of exposure to hazardous chemicals. Car battery recycling salvages raw materials that are still useful to be made into other products. At the same time, it protects you and your family from health hazards due to unintentional exposure.
How to Identify What Type of Battery You Have
The first step to proper battery disposal is identification. Knowing the type of car battery you have is crucial for recycling because each type contains varying hazardous materials that require specific handling and processing methods. Proper identification helps prevent contamination and ensures more efficient recycling.
Let’s take a look at some of the most common types of car batteries.
Lead-Acid
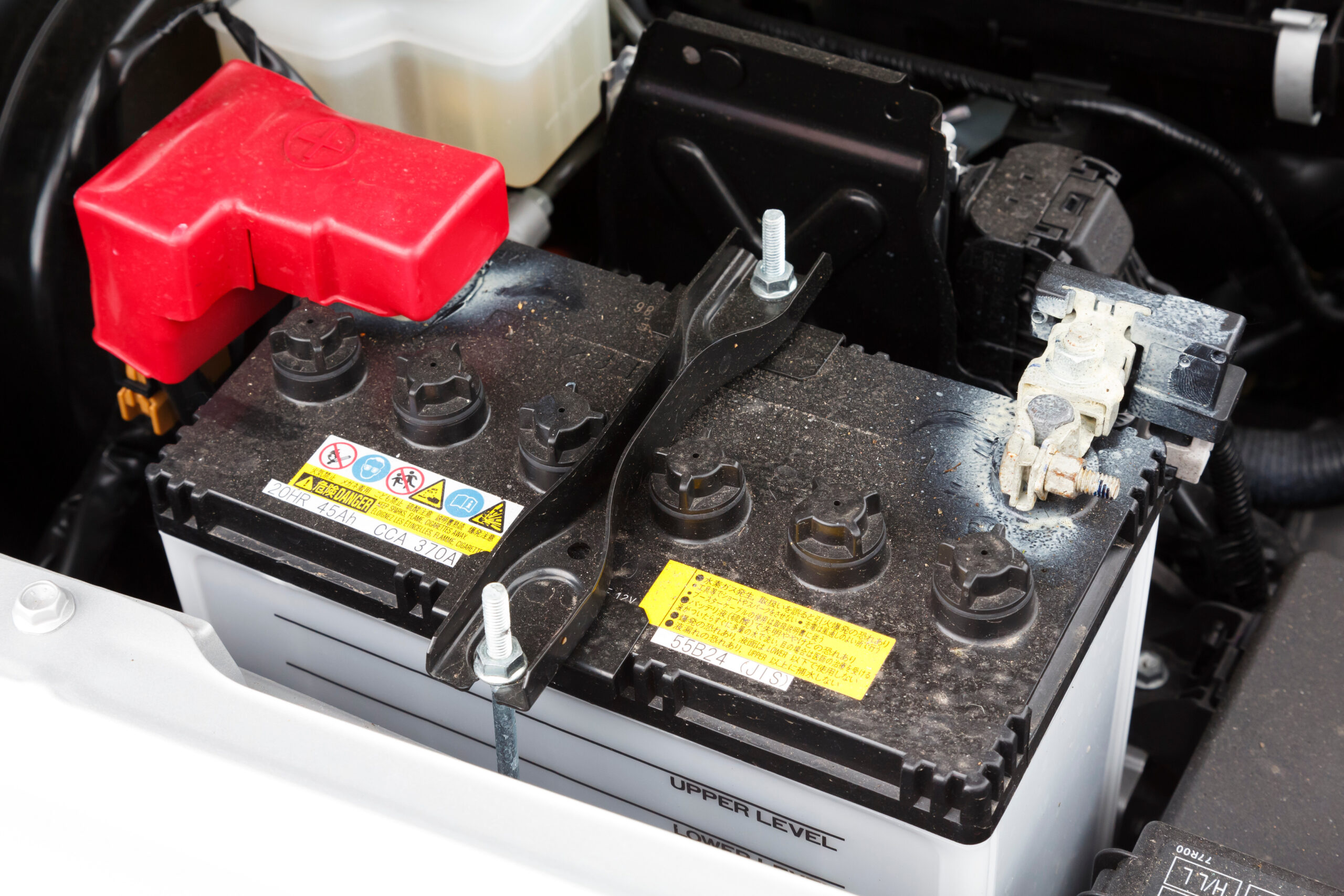

Lead acid batteries were first manufactured in 1859 and are considered the first rechargeable battery.
In lead-acid batteries, sulfuric acid is an electrolyte circulating between two separate lead-plate electrodes to generate electricity.
Lead-acid batteries are found in most conventional gasoline and diesel cars, commercial vehicles, motorcycles, and any other vehicle with a combustion engine. They are easily identifiable—they are typically bulky, have a heavy weight due to the lead content, and feature thick plastic casings. Often, you’ll find six or more caps on top for the cell compartments or a sealed top with no visible caps in maintenance-free models.
When handling this type of battery:
- First, inspect the battery for any signs of damage or leaks. Use extra caution if you notice damage.
- Always use gloves to protect against acid and lead exposure.
- Keep the battery away from open flames or sparks.
- Transport them in an upright position and secure them to prevent tipping.
- Store them in a cool, dry, and well-ventilated area to reduce the risk of gas accumulation.
AGM
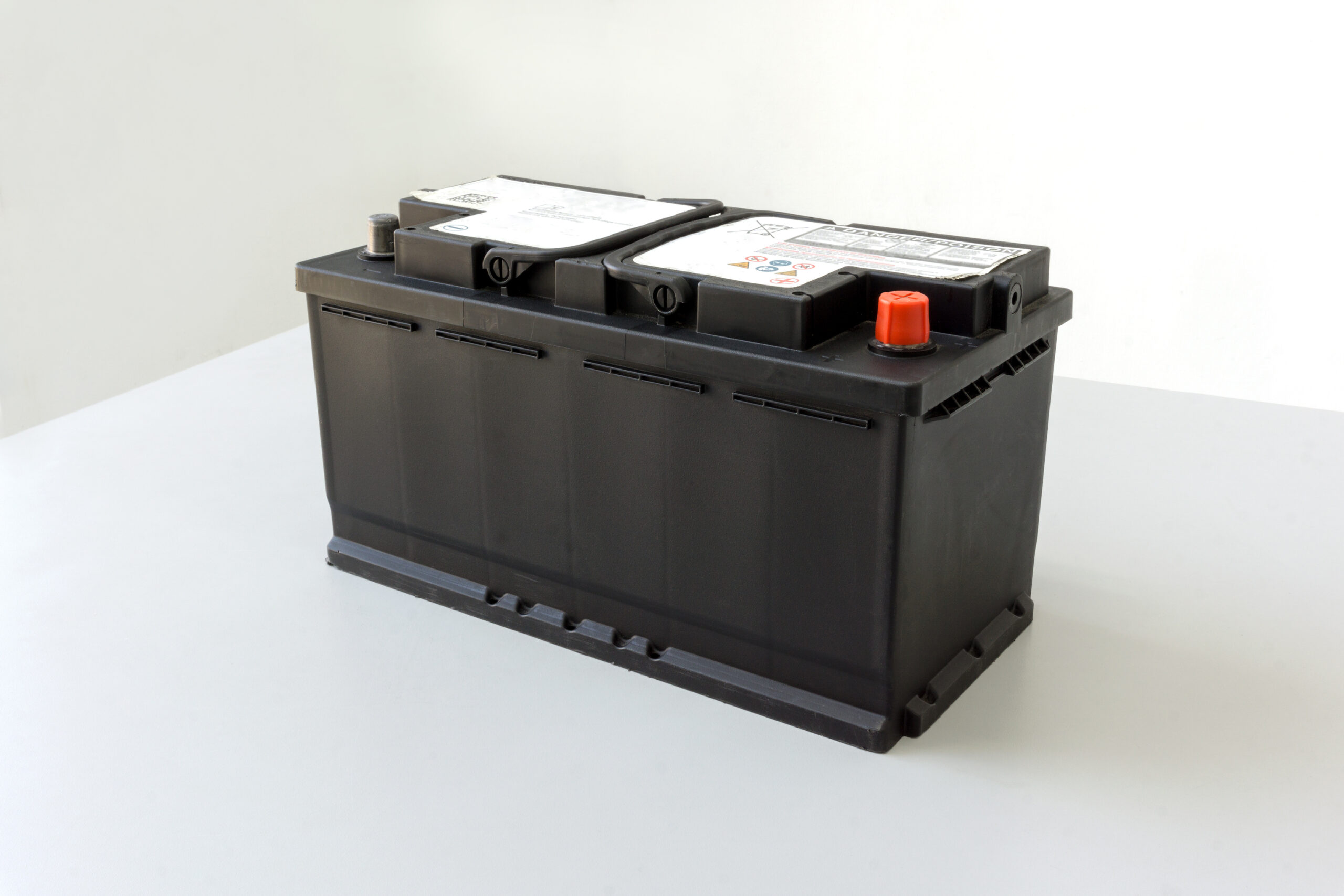

Absorbent Glass Mat (AGM) batteries are technically lead-acid batteries, but they have different design features from their traditional counterparts. They provide strong and ready power, recharge quickly, are low-maintenance, and last longer than lead-acid batteries.
While these batteries are most commonly used in passenger cars, they are also smart choices for ATVs, UTVs, boats, motorcycles, snowmobiles, and other powersport vehicles.
AGM batteries typically have a flat, rectangular shape and a sealed body, and they are often more compact than traditional lead-acid batteries. Additionally, because they are sealed, they do not have removable caps and are usually marked with the letters “AGM” or “Absorbent Glass Mat.”
General handling and storage tips for AGM batteries include:
- Wear gloves when handling.
- Store the battery in a cool, well-ventilated area away from any extreme heat sources, open flames, or sparks.
- Ensure you can safely handle the battery’s weight—dropping the battery could damage its internal structure.
Gel
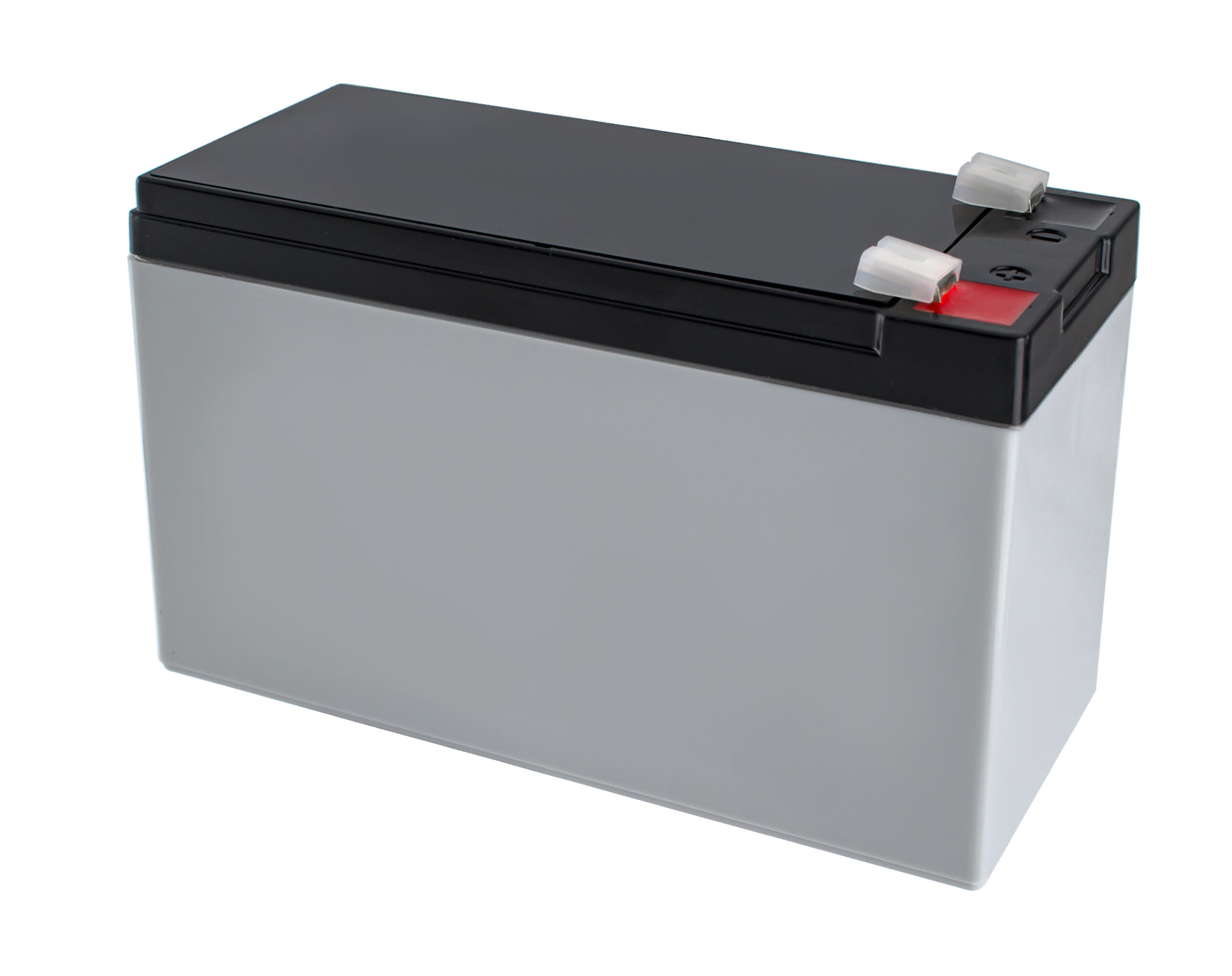

Gel batteries, also a subtype of lead-acid batteries, include a combination of sulfuric acid and fumed silica. This produces a firm, gel-like electrolyte substance that prevents spillage.
Their durability and very low maintenance requirements make them quite popular. They are commonly found in EVs, RVs, marine vehicles, wheelchairs, golf carts, and some high-end show cars.
Gel batteries typically have a similar shape to other lead-acid batteries (often rectangular) but are sealed, have a sturdy, impact-resistant plastic casing, and do not have removable caps. Similar to AGM, gel batteries are usually labeled with the word “Gel” or “Gel Cell” on the casing.
Handling tips for gel batteries are similar to those for other lead-acid types. Always inspect the battery for damage, wear gloves when handling it, and store it in a cool, well-ventilated area away from heat sources. When transporting them, ensure they remain upright and are unable to come into contact with conductive materials. If necessary, cover the terminals with insulating tape.
Lithium-Ion
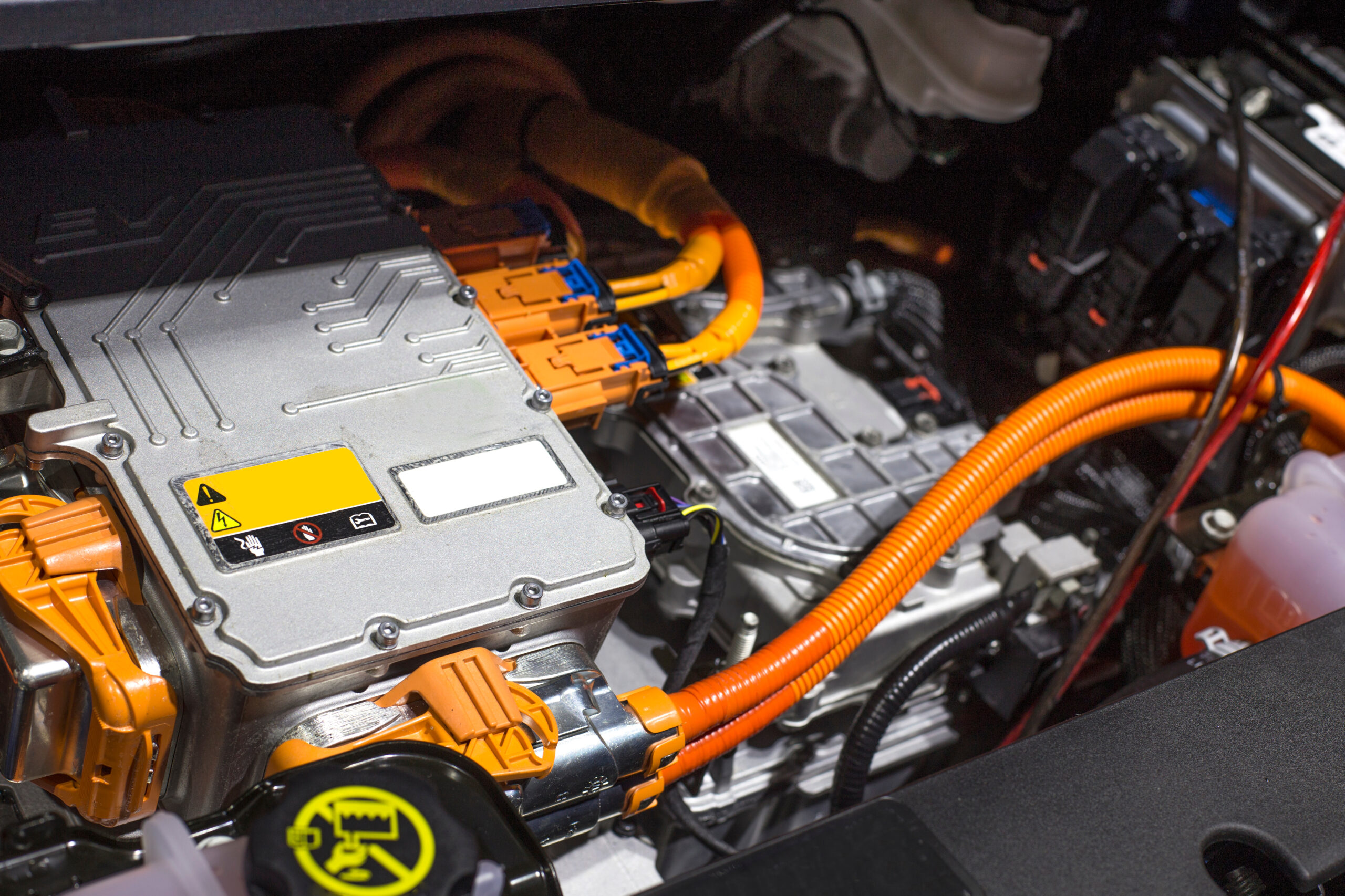
As the name suggests, a lithium-ion battery uses lithium ions as the main component of its electrolyte. The Li-ion battery industry is experiencing massive global expansion, and these batteries are increasingly used in numerous types of electric and hybrid vehicles.
Identifying a lithium-ion battery by shape can be difficult, as they can come in many shapes (cylindrical, rectangular, or flat), but they are usually labeled with “Li-ion” or “Lithium-ion.” You may also find voltage and capacity information printed on them.
When handling them:
- Ensure they’re at a charge level of around 30 to 50% before you take them to a recycling center.
- Safely handle with gloves, and do not drop. If the batteries are punctured, crushed, or bent, it can lead to internal short circuits.
- Store and transport the battery in non-conductive containers, and keep the containers in a cool place. Extreme heat can trigger thermal runaway, leading to fires or explosions.
- Tape over terminals with electrical tape before transport or storage to prevent short circuits.
- Never disassemble the battery on your own.
Nickel-Metal-Hydride
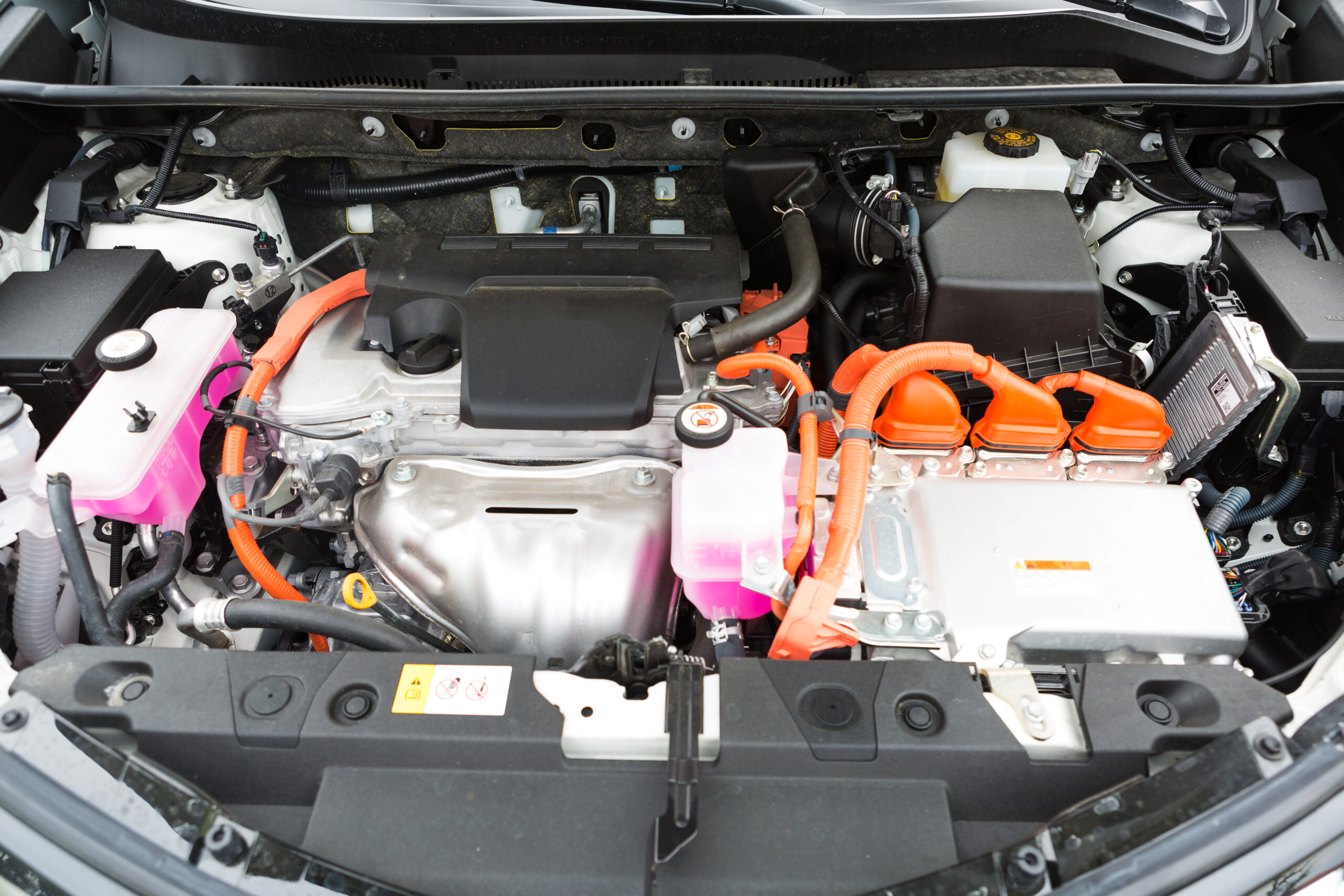

Nickel-metal-hydride (NiMH) batteries use older technology than modern Li-ion batteries, but they are still used in some popular passenger vehicles, like the AWD Prius and Toyota Sienna Hybrid. They are mainly used in hybrid EVs and less in EVs, HEVs, and PHEVs.
Appearance-wise, NiMH batteries are typically cylindrical or rectangular and labeled as “NiMH” or “Nickel-Metal-Hydride.”
NiMH batteries have the same handling, storage, and transportation recommendations as Li-ion batteries.
How to Safely Remove Your Battery
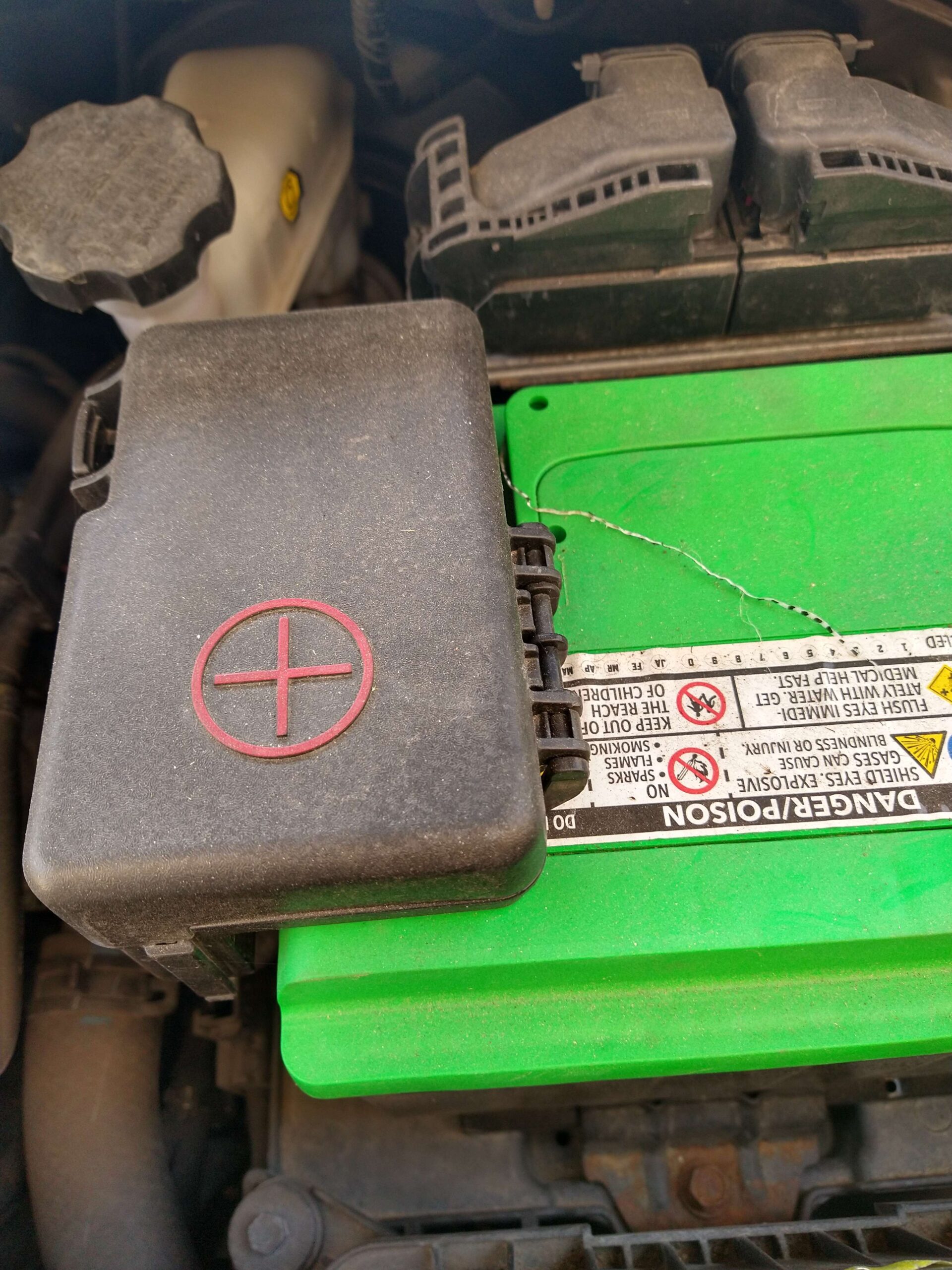

When removing/disconnecting a battery, you’ll need gloves, wrenches (terminal bolts are usually 10mm or 13mm), a socket set, pliers (for clamps that are tight or corroded), wire brushes (to address significant corrosion), and/or battery terminal pullers (if the terminals are very tight and cannot be removed by hand after loosening with a wrench).
- Ensure your car is off and your keys are not in the ignition.
- Open the hood and determine the precise location of the battery. It’s usually located in the front corner of the engine compartment, but in some cars, it might be located in the trunk or under a seat.
- Locate and disconnect the negative battery cable (marked with a minus sign or covered with a black cap). Use a wrench to loosen the bolt on the negative terminal clamp.
- Disconnect the positive battery cable (marked with a plus sign or covered with a red cap). Use a wrench to loosen the bolt on the clamp.
- Loosen and remove the hold-down clamp or bar if your battery has one. Use a socket wrench or pliers to remove these.
- Carefully remove the old battery from the vehicle. Many batteries are heavy—so maintain a good grip.
Make sure that the battery tray is cleaned out and ready to accept the new battery. You can use a wire brush to clean your terminal clamps and remove all corrosion from the assembly.
What Is the Proper Way to Handle, Store, & Transport a Car Battery?

It is best to recycle a car battery as soon as possible after replacing it. The longer it remains in storage, the greater the risk of harmful exposure.
General Handling Tips:
- Wear gloves.
- Don’t drop the battery.
General Storage Tips:
- Keep the battery in a cool, well-ventilated area.
- Keep the battery away from significant heat sources, such as flames and sparks.
- Store lead-acid type batteries in heavy-duty plastic bags to contain any potential leaks. If you do not have heavy-duty plastic bags, double wrap them with regular plastic bags.
- Store Li-ion and NiMh batteries in non-conductive containers.
- Keep the battery upright to prevent spillage.
General Transportation Tips:
- Keep the battery in its container or bag.
- Keep the battery in a secure, upright position—it shouldn’t move around a lot.
- Keep it away from heat and conductive sources.
Where Can You Recycle Your Car Battery?
You can recycle your old car batteries at High Tech Recycling. We accept both pickups and drop-offs. You can drop off your battery at our Pontiac, MI, location Monday through Friday between 9 a.m. and 5 p.m. If you want us to pick up your battery, please complete our online form today to schedule your appointment.
Please note that we cannot accept swollen car batteries.



























